Install Snort On Centos 7 Minimal
CentOS 7 Minimal x86_64 Base Installation Guide Updated article as of November 2017 at the URL below. • Revised: March 31, 2016. Added the 'Note' below. No other changes. Revised June 9, 2016. Provide link to newer document for CentOS 7. Canterville Ghost Movie 1996 Download Firefox there. 2.1511.
The purpose of this guide is provide the steps to build a standardized CentOS 7 build 1503 aka Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7.1 Minimal x86_64 base operating system. Note I am observing changes between minor versions that are significant. More specifically Red Hat's emphasis on systemd, firewalld, and NetworkManager ( mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00 inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6::1/128 scope host valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever 2: eno16777728: mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast state UP qlen 1000 link/ether 00:0c:29:ad:96:16 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff [root@localhost ~]# Note: CentOS 7 no longer uses the naming convention previously used for network interfaces, e.g. Eth0 or eth1. It now uses a designation as provided by the system BIOS. In the examples, eno16777728 is equivalent to interface eth0 found with CentOS 6 which results with the configuration file ifcfg-eno16777728 versus ifcfg-eth0.
Reference: The default configuration for the network interface, eno16777728, is given below. You may have a different DEVICE and will have a different UUID. [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eno16777728 TYPE=Ethernet BOOTPROTO=dhcp DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no NAME=eno16777728 UUID=05d5a7d5-f16e-4492-9ea1-fa46b7134a8a DEVICE=eno16777728 ONBOOT=no IPV6_PEERDNS=yes IPV6_PEERROUTES=yes IPV6_PRIVACY=no [root@localhost ~]# If you desire to use DHCP, update ifcfg-* using ONBOOT value from no to yes, save, then restart network services.
The purpose of this guide is provide the steps to build a standardized CentOS 7 build 1503 aka Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 7.1 Minimal x86_64 base operating system. This tutorial will guide you on how to perform a minimal installation of latest released version of CentOS 7.0, using the binary DVD ISO image.
Introduction There are few and straight forward administration guides are available for snort on the web. Today, we will try to explain anatomy of snort step by step. Snort is an NIDS (Network Intrusion and Detection System) used to detects and prevent intrusions over the network. Through protocol searching, content analysis and various preprocessors, snort detects thousands of worms and vulnerability attempts. Snort comes with an excellent feature including detection of various types of attacks, buffer overflow, stealth port scan, CGI Attacks etc.
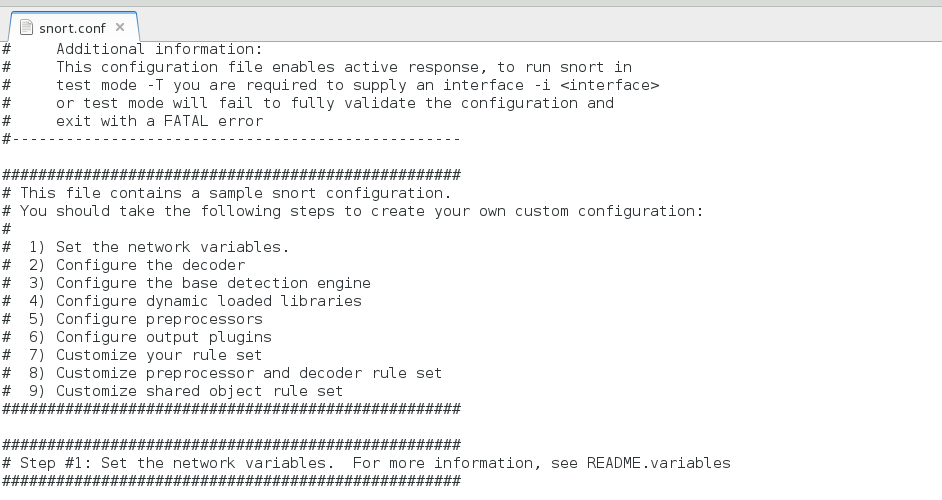
Configuration file of Snort configuration is /etc/snort/snort.conf in which information of network under investigation is determined. Sample configuration file Snort can be configured in three modes. Sniffer Mode Output will dump to the terminal in this mode, it is used to display packets in continuous flow to the user in live mode, in live mode or sniffer mode data packet losses are very high so it is recommended to used sniffer mode NIDS only for small networks only. Packet Logger Mode Output will get logged to the disk, which can be monitored later on. Snort -l is the option which is used for logging mode. Network IDS Mode In IDS mode some parameters are configured that allow snort to match defined parameters while scanning the network, parameters are used defined in this mode. Prerequisites for Installation Make sure that following packages are already installed with the system you are going to configure snort- CentOS 7.0, Snort latest, DAQ (Data Acquisition Package) Available with Snort.